We take for granted the gasoline (or diesel) we put in our cars and trucks is free from contaminants when pumped in to our gas tanks. The purity we've come to expect at the fuel pump didn't happen overnight. It took many years, and thousands of engineering hours, to develop the refining processes that produces today's clean gasoline and diesel.
Fuel Cell Vehicles are a category of electric vehicle (EV's). Fuel cell vehicles use hydrogen gas (H2) to power an electric motor. Unlike conventional vehicles which run on gasoline or diesel, fuel cell cars and trucks combine hydrogen and oxygen to produce electricity to drive the motor.
Similar to the path that gasoline and diesel processing took toward purity, the use of H2 as feedstock for fuel cells in transportation has driven requirements for H2 purity standards to very strict levels. This push has also elevated the need for cost-effective and reliable instruments that can sample H2 near the nozzle of a delivery pump, and either certify acceptability or provide a signal to shut off the fuel distribution system.
Duro-Sense Corporation, a California based manufacturer of high quality temperature sensors, is part of a team working under a DOE funded research program to develop a
Hydrogen Contamination Detector. The sensor, which will be installed at hydrogen fueling stations, will detect poor quality hydrogen gas before entering the fuel cell vehicle. The sensor is intended to detect multiple impurities at extremely low levels in hydrogen to prevent fuel cell performance degradation.
Duro-Sense is designated as the industrial partner and vendor aiding in defining the commercial manufacturability of the Hydrogen Contamination Detector.
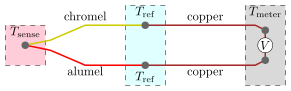
As part of their preliminary work, a thermocouple embodiment was selected as a cost-effective platform for the Hydrogen Contamination Detector because:
- Direct Commercial Availability
- Proven History of Reliability and Robustness
- Adaptability of Conductor Materials for Most
- Appropriate Catalyst for Each Contaminant
- Ability to Incorporate up to 12 Conductors a Single Thermocouple, Reducing Fluid Stream Penetrations
They also assisted with a high pressure pass-through to integrate the sensor into fluid stream to accommodate a pressure rating of 30,000 PSI using a cone and thread style fluid connection.
The Hydrogen Contamination Detector project is still in its very early stages, and research and development continues, subject to funding and continued interest in alternative fuel technology.