An RTD works by taking advantage of a simple physical principle: the electrical resistance of certain metals changes in a repeatable way as temperature changes. Most RTDs use platinum as the sensing element because it offers excellent chemical stability and a nearly linear resistance-to-temperature relationship. As temperature rises, the platinum's electrical resistance increases; as temperature falls, resistance decreases. Measurement electronics monitor this resistance change and convert it into an accurate temperature reading.
The basic design of an RTD centers on the sensing element, which is either a fine platinum wire wound around a ceramic or glass core, or a thin platinum film deposited on a flat substrate. Wire-wound RTDs tend to offer the highest accuracy and long-term stability, while thin-film RTDs provide faster response times and greater mechanical robustness. The element connects to lead wires, which carry the resistance signal back to the transmitter or control system. To protect the element from moisture, vibration, and corrosive environments, manufacturers typically encase RTDs in metal sheaths made from stainless steel or other specialized alloys.
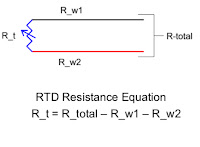
RTDs are commonly configured in two-wire, three-wire, or four-wire designs, depending on how much measurement accuracy the application demands. In simpler setups, lead wire resistance can influence the reading, especially over long cable runs. More advanced configurations compensate for that resistance, ensuring the temperature reading reflects the sensor element itself rather than the wiring. This flexibility makes RTDs suitable for everything from short laboratory connections to long-distance industrial installations.
Standard platinum RTDs are available in multiple accuracy classes, with Class B offering ±(0.3°C + 0.005|t|), Class A offering ±(0.15°C + 0.002|t|), and higher precision versions such as 1/10 DIN providing even tighter tolerances. This level of accuracy, combined with excellent long-term stability, makes RTDs particularly valuable in applications where precision matters more than extreme temperature range. While typical RTDs operate from -200°C to 850°C depending on construction, they often outperform thermocouples in low- to mid-temperature applications, especially when tight control and minimal drift are critical.
Process industries such as chemical processing, food and beverage production, pharmaceuticals, power generation, and water treatment all use RTDs to maintain consistent product quality and system performance. Engineers widely specify RTDs because their behavior is easy to explain, easy to model, and easy to trust. When accuracy, stability, and predictable performance define the application, RTDs remain a practical and proven choice for temperature measurement.